Radiographic errors are divided into two categories; operator errors and developing errors. Errors can result in misdiagnosis of dental disease and can also result in unnecessary exposure to the patient and the operator if retakes are required. Errors also occur if films are mounted inaccurately.
In the examples below, click on the pictures to enlarge them
OPERATOR ERRORS
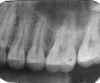
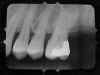
| Elongation: Occurs when there is insufficient vertical angulation of the tubehead (too flat). To correct, increase the vertical angulation of the tubehead. |
 |
 |
|
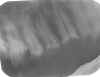
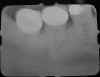
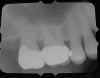
Foreshortening: Occurs when there is too much vertical angulation of the tubehead (too steep). To correct, decrease the vertical angulation of the tubehead. |
 |
 |
|
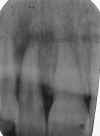
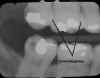
Overlapping: Occurs when horizontal angulation is incorrect. Correct by directing the central ray through the contacts of the teeth . See illustration |
|
|
|
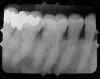
Conecut: The PID did not cover the entire film. To correct, be sure PID is placed correctly and centered over film. |
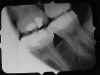
|
|
Incorrect settings: Timer, kVp or milliamperage was not set correctly. Verify that settings are correct before exposure. |
 underexposed |
 Overexposed |
|
Bent film: The patient bent the film upon closing. To correct, use film holding devices or cotton rolls to avoid bending and place the bite block next to the teeth before having patient close. |

|
|
|
Double Exposure : The same film was exposed twice. To prevent, make sure exposed films are placed in a separate location (a baggie, for example) |

|
|
|
Creased film: The film emulsion was cracked when the operator tried to soften the film corners by bending them. To avoid, gently round the corners rather than bending sharply. |

|
|
|
Blurred film: The patient or the tubehead moved during exposure. To correct, stabilize patient and tubehead before exposure. |

|
|
PROCESSING ERRORS
| Overlapped Films: Films were fed too quickly into processor. To correct, allow time before insertion of films into the processor. |
 |
|
| Fingerprint artifact: Caused by improper handling of film during processing. To correct, handle films by the edges only. |
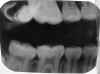 |
|
| Fingernail artifact: Caused by improper handling of film during processing. To correct, handle films by the edges only. |
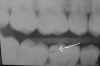 |
|
| Static electricity: Black lines caused by the creation of static electricity when film packets are opened too quickly. To correct, open film packets slowly. |
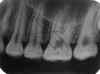 |
|
| Ghost Image: An artifact on the radiograph from earrings, jewerly, or metal caused by xray beam penetrating the object twice; appears radiopaque. |
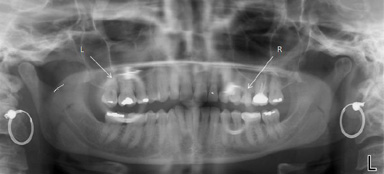 |
|